
Objective
- To understand “literal”.
- To understand “types”.
”Literals” and ”types” are the foundation of python. ”Literals” and ”types,” like ”operators,” are useful for understanding small changes in programs by knowing their roles and how to use them. They are important to keep in mind before learning about ”variables,” ”control structures,” ”classes,” ”file operations,” and so on.
Python Basics (Literals)
In the previous issue, we dealt with ”operators”. In this installment, we will learn about ”literals”. ”Literals” are unchangeable values used in programs.
Specifically, they are integers such as ”0” and ”23”, floating-point numbers such as ”56.0” and ”0.034,” strings such as ”abcdefg,” and python’s built-in constants such as “True” and “False”.
Literals are the values used for the operand in the previous study.
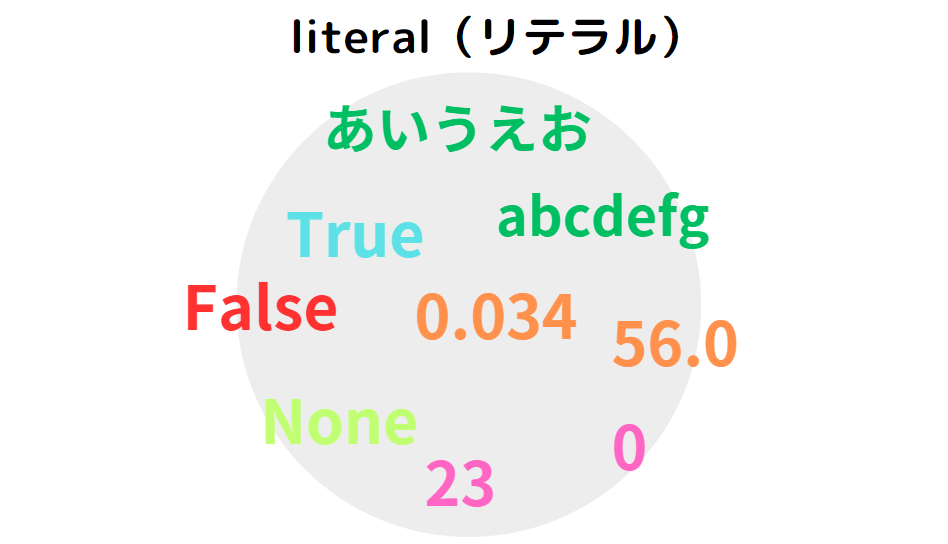
「Types of literals」
「Types of literals」
A ”literal” was an unchangeable value used in a program. These literals can be classified into several types. These can be broadly classified into ”numeric literals,” ”string literals,” ”built-in constants,” and ”other literals (lists, tuples, dictionaries, sets)”.
Numeric ”literals” can be further divided into ”integer literals” and ”floating-point literals”, and ”integer literals” into ”binary literals,” ”octal literals,” ”decimal literals,” and ”hexadecimal literals”.
| Literal Classification | Classification of classified literals | Notation |
| Numeric literals | Integer literals (binary literals) Binary numbers are prefixed with “0b”. | 0b10011 Available numbers are “0” and “1”. |
| Integer literals (octal literals) Octal numbers begin with the prefix “0o”. | 0o12345670 Available numbers are “0” to “7”. | |
| Integer literals (decimal literals) | 1234567890 Available numbers are “0” to “9”. | |
| Integer literals (hexadecimal literals) Hexadecimal numbers start with “0x”. | 0x1234567890abcdef Available numbers are “0” to “9” and a” to ”f”. | |
| Floating point number literals | 123.45 | |
| Imaginary literal | 3.14j | |
| String literals | String literal | ”abcdef” |
| Built-in constants | Boolean literal (True) | True |
| Boolean literal (False) | False | |
| None | None | |
| Other Literals | List | [1,2,3,4,5] |
| Tuple | (1,2,3,4,5) | |
| Dictionary | {key1:value1, key2:value2} | |
| Set | {1,2,3,4,5} |

Unchangeable Value
The meaning of “unchangeable value” expressed in the “explanation of literal” is that for values marked “1”, the value does not change its appearance.

python basics (types)
Literals have a “type” that describes their kind. A “type” is also a classification of literals and defines how the literal is to be handled. For example, a literal that represents a number can perform arithmetic operations.
| Type | Meaning |
| int | Integer type (in python, the number of digits a PC can handle is available) ※In other programming languages, the number of digits is fixed. |
| float | Floating point number type ※In other languages, there are “double” and “float” floating-point types, but only “float” is available in python. “float” in python is equivalent to “double” in other languages. |
| complex | complex type A type of imaginary literals. |
| str | String type |
| boolean | boolean True/False |
| list | list type |
| tuple | tuple type |
| dict | dictionary type |
| set | set type |
Using Literals and Checking Types
From here, I would like to use the “Interactive Shell” to manipulate “literals” and confirm “types”. Start the “Interactive Shell” and enter the following
We use “binary literals,” “octal literals,” “decimal literals,” and “hexadecimal literals” as integer literals. 0b10011” and ‘0o12345670’ are the respective literals. (The displayed “19” and “2739128” are also literals.)

The following uses floating-point number literals and imaginary literals.

The following uses string literals. String literals must be enclosed in “single quotes” or “double quotes”. Failure to do so will result in an error.
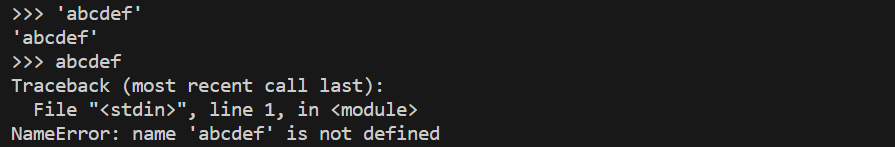
Boolean literals are built-in constants. They look like strings, but do not need to be enclosed in “single quotes” or the like.

The following input checks the “type” of a literal. The type function of the “built-in functions” is used to check the “type“.

That is all for this article.

ブックマークのすすめ
「ほわほわぶろぐ」を常に検索するのが面倒だという方はブックマークをお勧めします。ブックマークの設定は別記事にて掲載しています。



-640x360.jpg)

-640x360.png)
-640x360.png)
-640x360.jpg)
-640x360.jpg)

カスタム調査とシンジケートデータ-320x180.png)
帰無仮説と対立仮設・有意水準・P値・z検定-320x180.png)
準実験:合成コントロール法-320x180.jpg)
準実験:回帰不連続デザイン(RDD)-320x180.jpg)
準実験:傾向スコアマッチング(PSM)-320x180.jpg)